Abstract
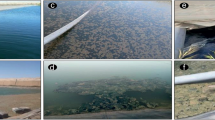
The macro-algae communities observed in the south lake of Tunis are characterized by the predominance of nitrophilous algae which are in the order of biomass importance:Ulva, Cladophora andEnteromorpha. We have noted seasonal changes of alga distribution. The wind appears to be one of the most important factors influencing this distribution. The total biomass reaches a maximum in the spring. Rapid decomposition of the biomass leads to a severe ecological imbalance, resulting in crises of anoxia and fish death.
A restoration project has already started. It aims at removal of contaminated muds and the introduction of a new circulation system.
The main objectives of this work were to collect information on the distribution and biomass of the phytobenthic communities as a first step in the constitution of a database for further comparison.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anon. 1991.Etude d'aménagement du lac sud de Tunis. SERAH & SOTINFOR Rapport Général. Direction des ports maritimes. Ministère de l'Equipement et de l'Habitat. Tunis, TN.
Belkhir, M. 1980.Eutrophisation du lac de Tunis: Etude physico-chimique et biomasses phytoplanctonique et macro-algale. Thèse 3ème cycle, Faculté des Sciences, Tunis, TN.
Belkhir, M. 1983. Notions d'hydrologie comparée dans le lac de Tunis et le Golfe de Tunis.Bull. Inst. Nat. Tech. Océanogr. Pêche Salammbô 10: 5–26.
Belkhir, M. 1984. Dynamique des peuplements algaux dans le lac de Tunis.Bull. Inst. Nat. Tech. Océanogr. Pêche Salammbô 11: 41–69.
Belkhir, M. & Hadj Ali Salem, M. 1981. Contribution à l'étude des mécanismes d'eutrophisation dans le lac de Tunis: évolution des paramètres physico-chimiques et biologiques.Bull. Inst. Nat. Sci. Tech. Océanogr. Pêche Salammbô 8: 81–98.
Ben Charrada, R. 1992. Le lac de Tunis après les aménagements. Paramètres physico-chimiques de l'eau et relation avec la croissance des macro-algues.Marine Life 1: 29–44.
Ben Maïz, N. 1993. Evolution des peuplements phytobenthiques après les travaux d'assainissement dans le lac Nord de Tunis. pp. 89–104 In: Boudouresque, C.F., Avon, M. & Pergent-Martin, Ch. (eds.)Qualité du milieu marin. Indicateurs biologiques et physico-chimiques, Gis Posidonie Publications, Fr.
Ben Maïz, N., Boudouresque, C.F. & Ouahchi, F. 1987. Inventaire des algues et phanérogames marines benthiques de la Tunisie.Giorn. Bot. Ital. 121: 259–304.
Caumette, P. 1985.Rôle des bactéries phototrophes et des bactéries sulfato-réductrices dans les milieux lagunaires. Etudes et thèses. Edit. ORSTOM, Paris, FR.
Comin, F.A., Menendez, M.L. & Lucena, J.R. 1990. Proposals for macrophyte restoration in eutrophic coastal lagoonsJ. Hydrobiol. 200/201: 427–436.
Comin, F.A., Menendez, M.L. & Martin, M. 1991. Short-term effects of decreasing water discharge on the chemical and biological characteristics of eutrophic coastal lagoons.Mem. Inst. Ital. Idrobiol. 48:9–22.
Heldt, H. 1929. Le lac de Tunis (partie nord): résultats des pêches au filet fin.Stat. Océanog. Salammbô 2: 1–76.
Menez, E.G. & Mathieson, A.C. 1981. The marine algae of Tunisia.Smithson. Contrib. Mar. Sci. 10: 1–59.
Ravera, O. 2000. The lagoon of Venice: the result of both natural factors and human influence.J. Limnol. 59: 19–30.
Runca, E., Bernstein, A., Postmac, L. & Di Silviod, G. 1996. Control of macro-algae blooms in the lagoon of Venice.Ocean Coastal Manage. 30: 235–257.
Schneider, W. 1977.Bilan des substances nutritives du lac de Tunis 1976/1977. Report Inst. Frésénius Gmbh, Minist. de l'Agriculture, Tunis, TN.
Sfriso, A. & Marcomini, A. 1996. Decline ofUlva growth in the lagoon of Venice.Bioresourse Technol. 58: 299–307.
Shili, A. 1995.Contribution à l'étude des peuplements à Ruppia (Monocotylédone, Potamogetonaceae) dans le lac nord de Tunis. D.E.A. (Diplôme d'Etude Approfondie) Faculté des Sciences, Université de Tunis, TN.
Stirn, J. 1966.Lac de Tunis Nord. Assainissement, Tome I, Etude et recherche, première partie Rapport Ministère de l'Agriculture, Tunis, TN.
Trabelsi, E.B. 1995.Contribution à l'étude des Chaetomorpha (algue Chlorophyceae) dans le lac nord de Tunis. D.E.A. Faculté des Sciences, Université de Tunis, TN.
Trabelsi, E.B., Shili, A. & Ben Maïz, N. 2001. Marine flora of the North lake of Tunis 12 years after its restoration. In: Özhan, E. (ed.)Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on the Mediterranean Coastal Environment. MEDCOAST 01, 23–27 October 2001, Hammamet, Tunisia, Vol. 2, pp. 915–922. Middle East Technical University, Ankara, TU.
Van Berk, A.H. & Oostinga, H. 1992. North lake of Tunis and its shores: Restauration and development.Terra Aqua 49: 23–32.
Verhoeven, J.T.A. 1979. The ecology ofRuppia dominated communites in Western Europe. I.-Distribution ofRuppia representatives in relation to their autecology.Aquat. Bot. 6: 197–268.
Zaouali, J. 1974.Les peuplements malacologiques dans les biocénoses lagunaires tunisiennes. Etude de l'espèce pionnièreCerastoderma glaucum Poiret (1789). Thèse de Doctorat d'Etat, Université de Caen, FR.
Zaouali, J. 1977. Le lac de Tunis: facteurs climatiques, physicochimiques et crises dystrophiques.Bull. Off. Natl. Pêch. Tunisie 1 (1): 37–49.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shili, A., Trabelsi, E.B. & Ben Maïz, N. Seasonal dynamics of macro-algae in the South Lake of Tunis. J Coast Conserv 8, 127–134 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1652/1400-0350(2002)008[0127:SDOMIT]2.0.CO;2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1652/1400-0350(2002)008[0127:SDOMIT]2.0.CO;2